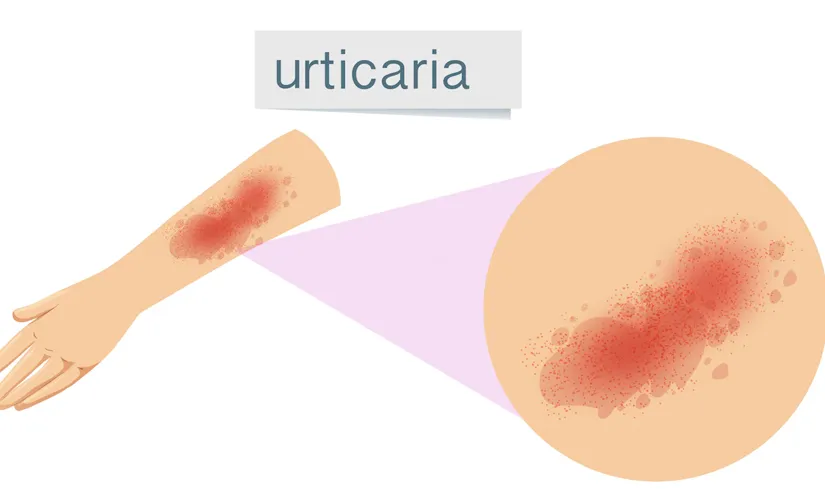
Urticaria is one of the most common skin diseases. It is also popularly known as hives. It consists of swollen, red, itchy lesions that change location within 24 hours. It may be widespread or localised. If it occurs suddenly and lasts less than 6 weeks, it is called acute urticaria, and if it lasts longer, it is called chronic urticaria. In acute urticaria, the causative factor is usually infection, drug use, etc., while in chronic urticaria, the cause is usually not found.
In the treatment, an oral medication group called antihistamines is used rather than creams. Several different subgroups of these drugs are used in the number of days recommended by your doctor. In acute cases, cortisone drugs can be used IM or orally. Again, drugs that reduce immunity, leukotriene receptor blockers, biological agents can be used in cases of persistent urticaria.
Again, we need to pay attention to our diet, especially in chronic urticaria. We should avoid gluten free, sugar and dairy products. We should also avoid situations that cause physical urticaria such as hot urticaria, cold or pressure urticaria.
